代謝内科学 Department of Metabolic Medicine
- 部門
- 総合医薬科学部門
- 分野
- 代謝・循環医学
- metab(アットマーク)kumamoto-u.ac.jp
スタッフ
| 教授 | 窪田 直人 nkubota0511(アットマーク)kumamoto-u.ac.jp |
|---|---|
| 講師 | 近藤 龍也(大学病院所属) t-kondo(アットマーク)gpo.kumamoto-u.ac.jp |
| 助教 | 阪口 雅司 msakaguchi(アットマーク)kumamoto-u.ac.jp |
| 助教 | 福田 一起 fukudakazuki(アットマーク)kumamoto-u.ac.jp |
研究テーマ
【研究プロジェクト名および概要】
代謝内科学講座では、糖尿病および代謝疾患、内分泌疾患における病態の分子生物学的解明を進めるとともに高度先進医療を目指した臨床研究を行っている。
(A) 糖尿病領域では、
(1) 2型糖尿病の病態の解明と新規治療法の開発
(2) 熱ストレス応答経路活性化とインスリン抵抗性・膵α/β 細胞機能・動脈硬化症の関連
(3) インスリン作用伝達分子の発現制御と疾患病態における意義
(4) 新規同定miRNA の糖尿病診療への応用
(B) 内分泌領域では、
(1) 原発性アルドステロン症に対する高感度診断法の開発
(2) 原発性アルドステロン症における炎症性サイトカインの役割
(3) 先端巨大症・成人成長ホルモン分泌不全症(AGHD)における糖代謝異常の検討
(C) 脂質代謝・動脈硬化・肥満領域では、
(1) マクロファージ増殖調節による動脈硬化進展阻止の研究
(2) 2 型糖尿病における非侵襲指尖部メイラード反応後期生成物(AGEs)含有量測定の臨床的有用性に関する研究
(3) 膵腺房細胞制御におけるインスリン作用の意義と新規糖代謝調節制御の解明
(4) 日本人の加齢による2 型糖尿病発症機序の解明(合志スタディ)
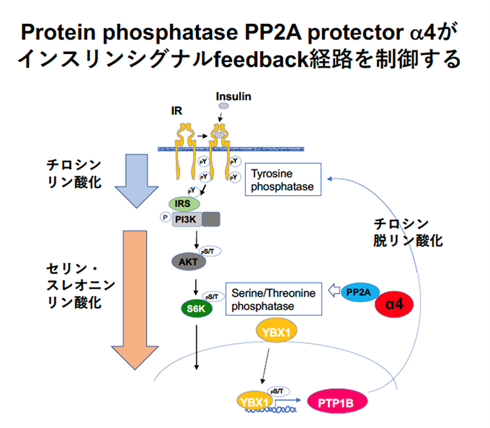
糖尿病、メタボリック症候群は全身組織のインスリン抵抗性に起因する。インスリンが受容体に結合すると、受容体のチロシンのリン酸化酵素が活性化する。その結果、細胞質内でセリン/スレオニンのリン酸化酵素を活性化して核内へシグナルを伝達する。細胞がインスリンに反応できるためには、常にインスリン受容体のチロシンリン酸化が脱リン酸化されていることが必要である。受容体のチロシン脱リン酸化酵素としてPTP1B が見つかっていたが、どのようにインスリン受容体のリン酸化レベルを制御しているのかは不明であった。我々は、インスリンシグナルの下流でセリン/スレオニン脱リン酸化酵素から上流のチロシン脱リン酸化酵素PTP1B 制御に連結するalpha4(α4)分子を見出しました。インスリンシグナルのフィードバック制御ループが明らかになり、インスリン抵抗性機序の解明に繋がる発見となりました。
文献:Sakaguchi M, et. al. Phosphatase Protector Alpha4 (α4) is involved in Adipocyte Maintenance andMitochondrial Homeostasis through Regulation of Insulin Signaling.
Nature Communications 13(1):6092, (2022).
In the Department of Metabolic Medicine, we are conducting clinical research aimed at advanced medical
care by advancing the molecular biological elucidation of pathological conditions in diabetes, metabolic
diseases, and endocrine diseases.
In the field of diabetes, we are focusing on the studies of the
(1) Elucidation of the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and development of new treatments
(2) Relationship between heat stress response pathway activation and insulin resistance, pancreatic α/β cell
function, and arteriosclerosis
(3) Regulation of insulin action transmitter expression and its significance in disease pathology
(4) Application of newly identified miRNAs to diabetes treatmen
In the field of endocrinology, we are focusing on the studies of the
(1) Development of a highly sensitive diagnostic method for primary aldosteronism
(2) Role of inflammatory cytokines in primary aldosteronism
(3) Pathophysiology of glucose intolerance in acromegaly.
In the field of lipid metabolism, atherosclerosis and obesity, we are focusing on the studies of the
(1) Research on preventing the progression of arteriosclerosis by regulating macrophage proliferation
(2) Research on the clinical utility of non-invasive fingertip Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
content measurement in type 2 diabetes
(3) Research on the significance of insulin action in the regulation of pancreatic acinar cells
(4) Elucidation of the onset mechanism of type 2 diabetes due to aging in Japanese